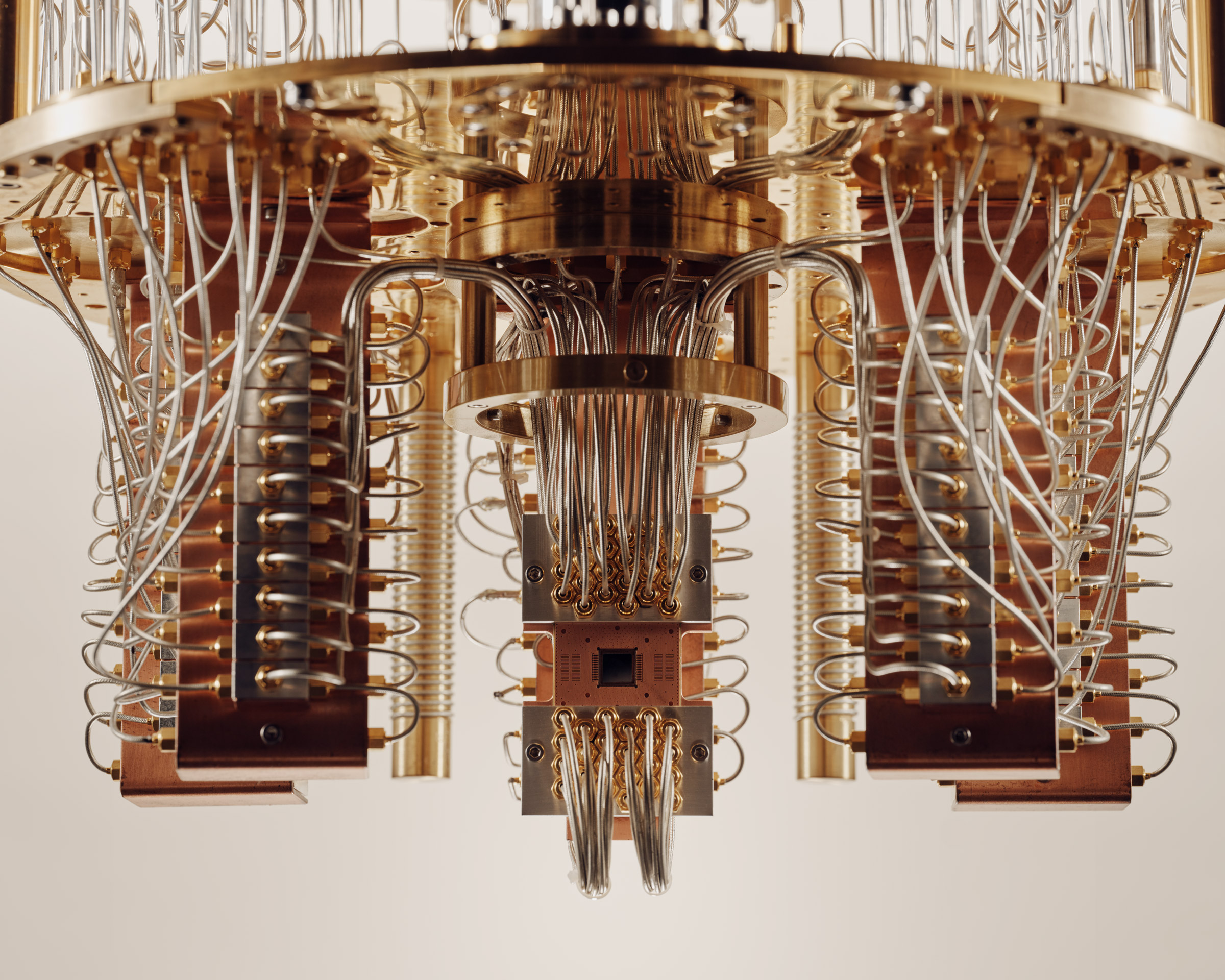
Quantum computing is a field of computer science that studies the use of quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform computation. It differs from classical computing in several ways.
Classical computers store and process information using bits, which are binary units of information that can be either 0 or 1. In contrast, quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This property, known as superposition, allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations much faster than classical computers.
Another key concept in quantum computing is entanglement, which occurs when two qubits are correlated in such a way that the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of the other, even when separated by large distances. This allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations that would be impractical or impossible for classical computers.